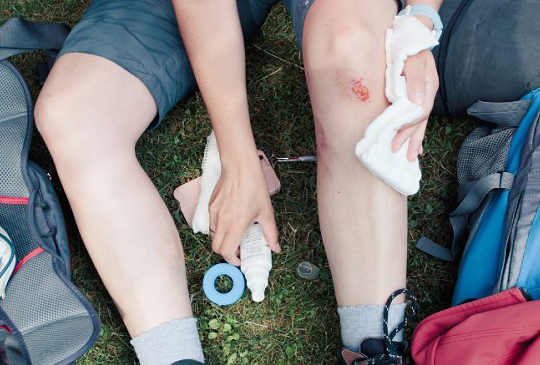
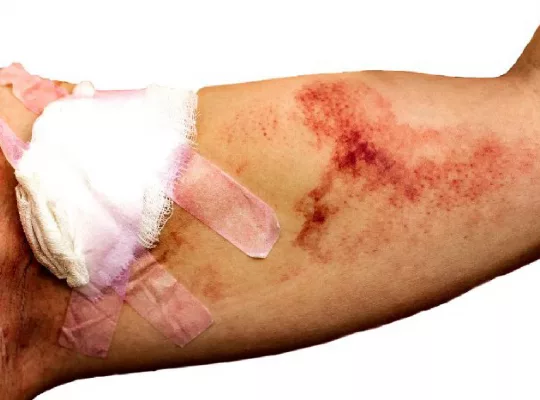
Caring for a wound might seem straightforward, but each type of wound has unique needs for proper healing. Without the right steps, wounds can become infected, leaving scars or even causing serious health issues.
For anyone unsure of the best approach, understanding the stages of wound care is essential. From cleaning and dressing to advanced methods for deep or complex wounds, knowing each stage can make a real difference. Did you know that wound infections can increase healing time by up to 60%?
In this guide, we’ll break down each stage of wound care, making it easier to handle cuts, scrapes, and other injuries safely and effectively.
Wound Healing Stages
The stages of wound care refer to the process of managing and treating wounds at different stages of healing. The four stages of wound healing are:
- Hemostasis: This is the initial stage of wound healing and occurs immediately after the injury. At this stage, the body begins to form a clot to stop bleeding and seal the wound.
- Inflammatory: This stage begins within hours of the injury and can last up to several days. During this stage, the body’s immune system sends white blood cells to the wound site to fight off infection and remove damaged tissue.
- Proliferative: This stage can last from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the wound. During this stage, new tissue begins to form, and the wound gradually closes.
- Maturation: This is the final stage of wound healing and can last for several months. During this stage, the new tissue becomes stronger and more resilient, and the scar becomes less noticeable.
Effective wound care involves assessing the wound at each stage of healing, cleaning and dressing the wound appropriately, and monitoring the healing progress.
Wound Treatment Stages
The stages of treating wounds involve a comprehensive process to ensure proper wound care and healing. These stages include:
- Assessment: The first step in treating a wound is to assess its severity and determine the appropriate course of treatment. This may involve evaluating the depth and size of the wound, the presence of any foreign objects, and signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Cleaning: Proper wound cleaning is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. This may involve washing the wound with sterile saline solution, removing any debris or foreign objects, and applying an antiseptic solution or ointment.
- Dressing: The type of dressing used will depend on the stage of wound healing and the severity of the wound. Dressings may range from simple adhesive wound closure strips for minor cuts and scrapes to more advanced dressings for deeper wounds.
- Monitoring: Monitoring the wound is crucial to ensure that it is healing properly and to detect any signs of infection or complications. This may involve checking the wound daily for changes in size, color, or drainage and seeking medical attention if necessary.
- Follow-up care: Once the wound has healed, follow-up care may be necessary to monitor for any long-term effects, such as scarring or impaired function.
How To Manage Pain
Here are some ways to manage pain associated with wounds:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Prescription pain medication: For more severe pain, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication such as opioids. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions and not exceed the recommended dose.
- Topical analgesics: These are creams or ointments that can be applied directly to the skin to reduce pain.
- R.I.C.E method: Rest, ice, compression, and elevation can help reduce pain and swelling associated with some types of wounds.
- Relaxation techniques: Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or visualization can help reduce stress and pain associated with wounds.
Always consult with your healthcare provider before taking any medication or starting any pain management techniques.
Assessing The Severity Of A Wound
Assessing the severity of a wound is important in determining the appropriate course of treatment. Here are some ways to know how severe a wound is:
- Look at the depth of the wound: A wound that is deep and extends through multiple layers of tissue is more severe than a shallow wound that only affects the top layer of skin.
- Check the size of the wound: A large wound may require medical attention and more extensive treatment than a small wound.
- Evaluate the location of the wound: A wound located in a critical area such as the face, neck, or chest may be more severe than a wound in a less critical area.
- Consider the cause of the wound: Wounds caused by sharp objects, such as knives or glass, are generally more severe than wounds caused by blunt trauma, such as a fall or impact.
- Observe signs of infection: Signs of infection such as redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge can indicate a more severe wound.
When Should You Access Medical Assistance?
You should seek medical assistance for a wound under the following circumstances:
- The wound is deep, long, or wide.
- The wound is bleeding heavily and the bleeding does not stop after applying pressure for 10-15 minutes.
- The wound was caused by an animal bite, a dirty or rusty object, or a human bite.
- The wound is located on the face, near the eyes, or over a joint.
- The wound shows signs of infection such as redness, warmth, swelling, pus, or increased pain.
- You have a fever or chills.
- You have not had a tetanus shot within the last 10 years.
- The wound is not healing or shows signs of becoming worse.
How to Prevent the Infection?
Preventing infection is an important aspect of wound care. Here are some ways to prevent infection:
- Keep the wound clean: Proper cleaning of the wound is essential to prevent infection. Clean the wound with soap and water or a saline solution and remove any dirt or debris.
- Cover the wound: Keep the wound covered with an appropriate dressing to protect it from dirt, bacteria, and other contaminants.
- Wash your hands: Wash your hands with soap and water before and after caring for a wound to prevent the spread of germs.
- Change the dressing regularly: Change the dressing regularly or as instructed by your healthcare provider to keep the wound clean and dry.
- Avoid touching the wound: Avoid touching the wound with your hands or other objects to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Avoid swimming or soaking in water: Avoid swimming or soaking in water until the wound is completely healed to prevent exposure to bacteria and other contaminants.
- Watch for signs of infection: Signs of infection include redness, swelling, warmth, pus, or increased pain. If you notice any of these signs, seek medical attention immediately.
Final Thoughts
Effective wound care is crucial for promoting healing and preventing infection.
Understanding the stages of wound healing and following proper wound care techniques can help ensure the best possible outcome for the wound.
It is important to keep the wound clean, apply appropriate dressing, change the dressing regularly, keep the wound moist, manage pain, and watch for signs of infection.
Seeking medical assistance when necessary is also important to ensure proper treatment for more severe wounds.
By taking these steps, we can help promote healing and prevent complications associated with wounds.
FAQs
Why Is The Inflammatory Stage Important?
The inflammatory stage is crucial for wound healing as it involves white blood cells that clear bacteria and debris. This process reduces the risk of infection and creates a suitable environment for new tissue growth, ensuring optimal healing conditions for the affected area.
What Occurs In The Proliferative Stage?
During the proliferative stage, new tissue formation occurs as fibroblasts generate collagen. This stage is characterized by the growth of blood vessels, which supply essential nutrients to the healing area. Additionally, the wound gradually contracts, contributing to the overall healing process and restoring the skin’s integrity.
What Is The Purpose Of The Maturation Stage?
The maturation stage focuses on collagen fibers strengthening and aligning to form scar tissue. Over time, this tissue increases tensile strength and elasticity, improving the wound’s durability. This stage is vital for restoring the functionality and appearance of the skin after injury.
What Are Common Signs Of Infection In A Wound?
Common signs of infection in a wound include increased redness, swelling, pain, foul odor, and pus discharge. If any of these symptoms arise, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure effective treatment of the infection.