Flu season is upon us once again, and you may be wondering about which thermometers are the most accurate and safest to use for children. This blog is to help you choose the best option.
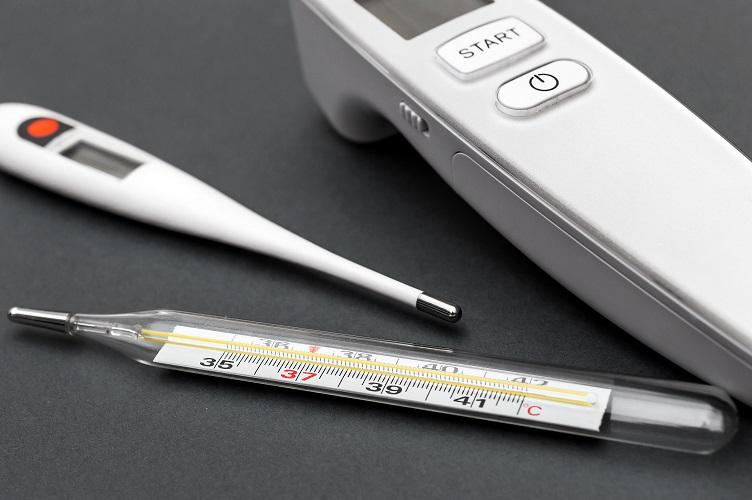
What Are The Different Types of Thermometers?
Digital Oral
Digital Ear
Rectal
Which Thermometer is The Most Accurate?
There are different types of thermometers. Medical professionals have determined that digital thermometers, specifically rectal thermometers, are the most accurate. Glass thermometers are not very reliable and are potentially hazardous. Forehead strips are the least accurate method, and should be avoided. IR thermometers are also very accurate and the best option for clinical use since they don’t require contact with the patient to work.
Which Thermometers Should You Use For Children?
For children under 6 months of age, a digital thermometer is the best option. After 6 months, digital ear thermometers are safe to use. Once your child is at least four years old, then they can start using oral ones.
While using a rectal thermometer on your child may not seem pleasant, pediatricians actually recommend this method since it is very accurate and very safe. Using a digital thermometer for an armpit temperature is also a good method, but is slightly less accurate.
How Does an IR Thermometer Work?
All warm-blooded animals give off energy as heat, and that heat is visible in the infrared (IR) spectrum. An IR thermometer is able to compare the heat being given off from a person and the heat of the surrounding environment. These comparisons are very accurate and even work in hot environments (Source).
Why Are Thermometers Important?
Being able to properly detect a fever is a key means of diagnosing and treating illnesses. Fevers themselves are not dangerous, but are signs for potentially dangerous illnesses and infections, especially in infants. The (rectal) temperatures to watch out for with infants are 100.4 F when under 3 months, 102 F with changes in mood or behavior from 3 to 6 months, and 102 F with secondary symptoms such as diarrhea, runny nose, etc. (source).