Lumps in the palm of the hand can cause discomfort, limit movement, and disrupt daily tasks. These small nodules or bumps may be alarming, especially when they lead to pain or restrict simple activities like gripping or holding objects.
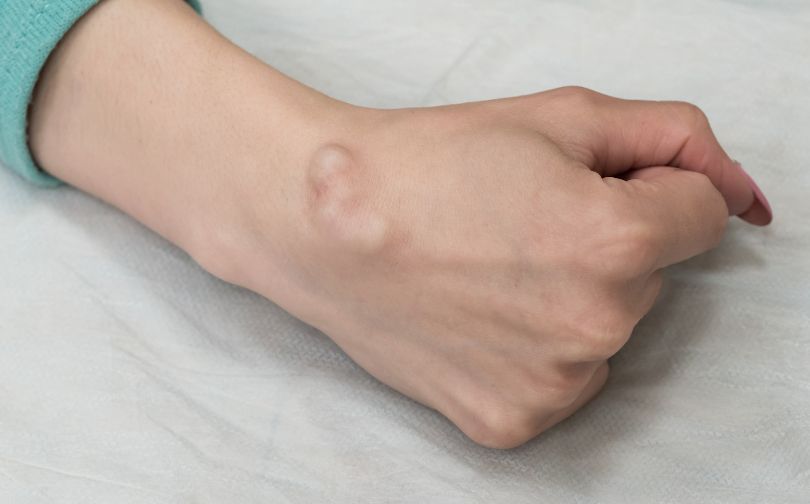
One common cause is Dupuytren’s contracture, a condition affecting the connective tissue beneath the skin. It can start as a lump, eventually pulling fingers into a bent position if untreated.
People often struggle with knowing whether to seek medical advice or manage the problem at home. It’s natural to worry when a lump appears without warning, but finding clear answers can ease those concerns.
In this guide, we’ll walk through possible causes, when it’s time to see a doctor, and how treatment options can help regain comfort and mobility. Stay with us as we clarify the steps to understanding and addressing this issue.
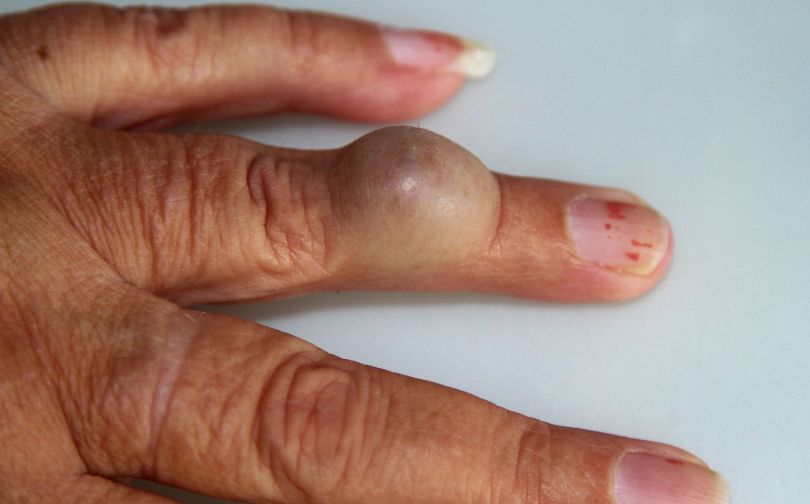
Ganglion Cysts
These fluid-filled sacs commonly develop near joints or tendons in the palm. They often appear as small, round lumps that may be firm or spongy to the touch.
Ganglion cysts are typically benign and may fluctuate in size. While the exact cause is unknown, repetitive stress or joint irritation is believed to contribute to their formation.
Treatment options include observation, aspiration (fluid removal), or surgical removal for persistent or symptomatic cysts, and consulting a physician is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Epidermal Inclusion Cysts
Epidermal inclusion cysts are noncancerous growths that develop beneath the skin’s surface in the palm. These cysts form when skin cells become trapped, leading to the formation of a small, round lump.
The cysts are usually painless but can cause discomfort if they become infected or inflamed. Treatment options include observation, drainage of the cyst’s contents, or complete surgical removal.
Again, consulting a physician is essential to evaluate and determine the most appropriate course of action for epidermal inclusion cysts in the palm.
Lipomas
Lipomas are benign tumors composed of fatty tissue that can develop in the palm and which typically feel soft and rubbery to the touch and are usually painless.
While the exact cause is unknown, they are believed to be associated with genetic factors.
Lipomas in the palm are generally harmless and may not require treatment unless they cause discomfort or affect hand function. In such cases, surgical removal may be recommended by a physician.
Dupuytren’s Contracture
Dupuytren’s contracture is a condition characterized by the thickening and contracture of tissue beneath the skin of the palm.
As the condition progresses, it can cause lumps or nodules to form in the palm, resulting in the fingers being pulled into a bent position.
The exact cause of Dupuytren’s contracture is unclear, but it is more common in individuals with a family history of the condition and those of Northern European descent.
Treatment options range from observation and hand exercises to surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the contracture and its impact on hand function.
Rheumatoid Nodules
Rheumatoid nodules are firm lumps that develop under the skin in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. These nodules can occur in various parts of the body, including the palms.
They are typically painless but can sometimes cause tenderness or discomfort. Rheumatoid nodules are associated with chronic inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment focuses on managing the underlying arthritis and may include medications to reduce inflammation, while, in some cases, surgical removal of the nodules may be necessary if they cause significant symptoms or impair hand function.
Foreign Body Granuloma
A foreign body granuloma is an inflammatory response that occurs when a foreign object, such as a splinter or glass fragment, becomes embedded in the palm.
This can lead to the formation of a lump or bump. The body’s immune system reacts to the foreign material, resulting in inflammation and the development of granulation tissue.
Treatment involves removing the foreign object, often through a minor surgical procedure, followed by appropriate wound care to promote healing and prevent infection.
Giant Cell Tumors Of The Tendon Sheath
Giant cell tumors of the tendon sheath are benign tumors that can develop near the tendons in the palm.
These tumors typically present as firm, painless lumps that may grow slowly over time. While the exact cause is unknown, they are thought to be related to chronic irritation or inflammation of the tendon sheath.
As for their treatment, it usually involves surgical removal of the tumor, particularly if it causes discomfort or affects hand function.
Fibromas
Fibromas are benign tumors that originate from connective tissue and can occur in the palm. These tumors are typically slow-growing and present as firm, nodular lumps beneath the skin.
While the cause of fibromas is unclear, they are generally considered to be noncancerous and do not metastasize.
Treatment options for palm fibromas depend on factors such as size, location, and symptoms, and surgical excision may be recommended if the fibroma is causing pain, interfering with hand function, or for cosmetic reasons.
Neurofibromas
Neurofibromas are noncancerous growths that develop on nerves and can occur in the palm. These tumors are associated with a genetic condition called neurofibromatosis.
They typically appear as soft, fleshy lumps and may cause pain or discomfort, especially if they press on nearby structures, while their treatment options depend on the size, location, and symptoms of the neurofibromas.
Infections
Finally, various infections can lead to the development of lumps in the palm, such as abscesses or cellulitis.
These infections may occur due to bacteria entering the palm through a cut, wound, or other means, and the symptoms of infected lumps can include redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and the presence of pus.
Therefore, prompt medical attention is necessary to diagnose and treat the infection appropriately, with the treatment typically involving antibiotics, drainage of abscesses, and proper wound care.
When Should I Seek Medical Attention for Lumps in My Hand?
If you notice a lump on your hand, it’s important to monitor it closely and seek medical attention in certain situations. One reason to consult a healthcare provider is if the lump grows rapidly. Sudden changes in size can be a sign of a condition that requires professional evaluation.
Pain is another indicator that warrants medical advice. A painful lump might suggest an underlying issue that should be addressed. Similarly, if you experience symptoms like numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, or difficulty moving your hand or fingers, it’s advisable to see a doctor. These symptoms could indicate that the lump is pressing on nerves or affecting other structures in the hand.
Signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or the presence of pus, also require immediate medical attention. Infections can lead to complications if left untreated, so it’s important to address these symptoms promptly. Lastly, if the lump is located in a spot that is easily irritated or interferes with your daily activities, it should be evaluated. Such lumps may cause discomfort or limit hand function, which might require treatment or removal.
The Bottom Line
nderstanding the various causes of lumps in the palm can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. Each condition, whether a cyst, tumor, or infection, presents unique characteristics, and careful monitoring is essential.
If any lump causes pain, discomfort, or restricts hand movement, consulting a healthcare provider is necessary. Timely evaluation ensures appropriate treatment, helping to restore comfort and function.
By addressing concerns early, it becomes easier to manage these conditions and reduce any potential impact on daily life. Taking proactive steps leads to better outcomes and minimizes the likelihood of complications. Therefore, staying attentive to any changes in the hands can be key to maintaining long-term health and well-being.
FAQs
What Are Common Causes of Lumps in the Palm of the Hand?
Common causes of lumps in the palm include ganglion cysts and Dupuytren’s nodules. Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled sacs often linked to joint or tendon irritation. Dupuytren’s nodules form due to Dupuytren’s contracture, where thickened tissue under the skin can lead to curled fingers.
What Treatments Are Available for Lumps in the Palm of the Hand?
Treatment depends on the cause. Ganglion cysts can be observed, drained, or surgically removed. Dupuytren’s contracture may require steroid injections or surgery to release contracted tissue. Other options for Dupuytren’s include enzyme injections or radiation therapy, especially in early stages, to manage symptoms effectively.
Can lumps in the palm resolve on their own?
Certain lumps, such as ganglion cysts, may resolve without intervention. However, conditions like Dupuytren’s contracture generally worsen over time and often require medical treatment if they begin to affect hand function or cause discomfort, limiting self-resolution potential.
Can Arthritis Cause Lumps in the Hand?
Yes, arthritis can cause lumps in the hand. Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis often lead to the formation of nodules or bony growths around joints, causing swelling and discomfort. These lumps result from chronic inflammation or joint degeneration, commonly affecting joint movement and function.